When you or a loved one are told a lung biopsy may be necessary, the words alone can send anxiety soaring. Understanding what this procedure is can bring clarity and peace of mind.
At Neumark Lung & Chest Surgery Centre, we focus on minimally invasive and precise approaches, ensuring our patients receive an accurate diagnosis and a smoother recovery.
What Is a Lung Biopsy?
A lung biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small piece of lung tissue is removed for laboratory testing and analysis. The tissue sample is examined under a microscope to detect infections, inflammatory conditions, or cancerous changes. A lung biopsy is often the most reliable way to confirm a diagnosis when imaging scans can’t give a clear answer.
While a chest X-ray or CT scan is a great initial test to spot nodules, they can’t always distinguish between benign conditions, infections and malignant tumours. That’s where a lung biopsy comes in, giving doctors the information they need to make an accurate diagnosis.
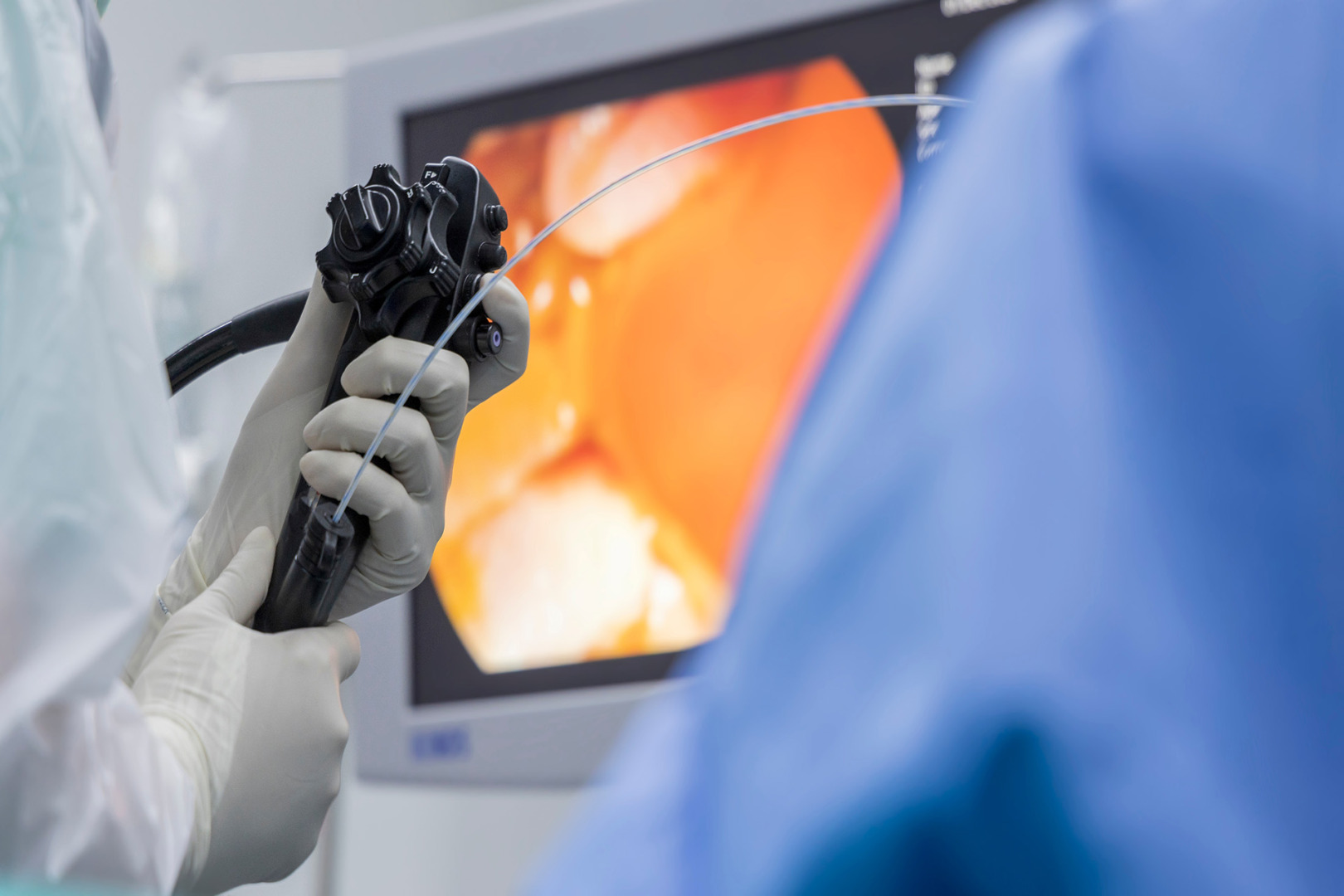
Why a Lung Biopsy Is Performed
There are several reasons why your specialist may recommend a biopsy.
Among the most common are:
- Lung Nodules or Masses: To see if a new nodule is benign or malignant.
- Suspected Lung Cancer: To confirm the presence of cancer cells and type.
- Infections: In some cases, when unusual or persistent lung infections occur, a biopsy can help pinpoint the cause.
- Inflammatory or Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like sarcoidosis or pulmonary fibrosis often require tissue analysis for diagnosis.
Early and accurate results from a lung biopsy can lead to earlier intervention, more targeted treatment, and improved patient outcomes.
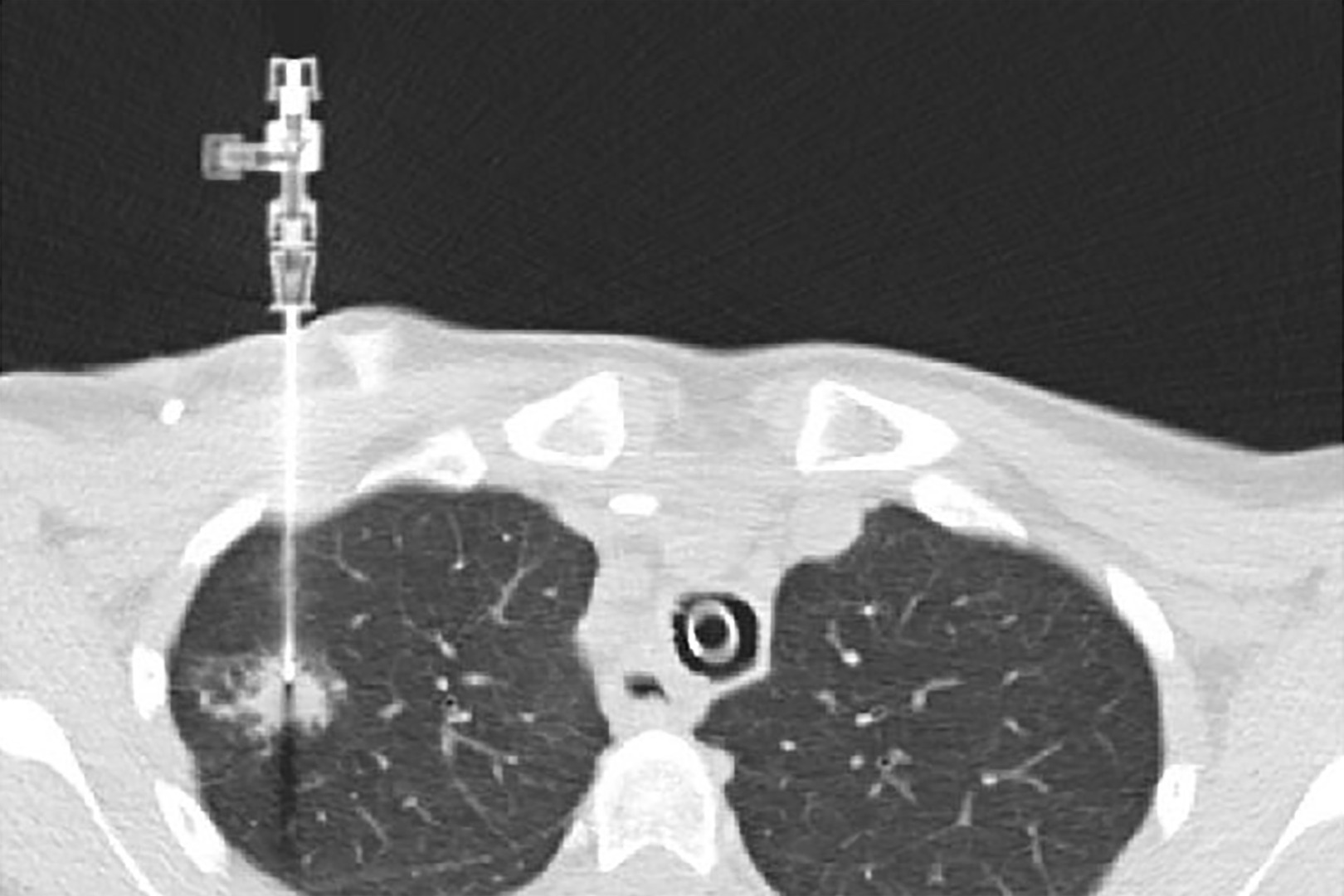
Types of Lung Biopsy Procedures
Not all lung biopsy procedures are the same. The technique used depends on the size and location of the abnormality, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Bronchoscopic Biopsy
A bronchoscope is a thin, flexible tube inserted through the mouth or nose, down into the lungs. Using a camera and tiny tools, the surgeon can take samples from the airways or nearby tissues. This is a minimally invasive procedure and is often used for lesions near the larger airways.
Needle Biopsy (CT-Guided)
Also known as transthoracic needle aspiration, this involves inserting a needle through the chest wall into the lung, guided by CT imaging. It’s typically used for nodules in the outer parts of the lung.
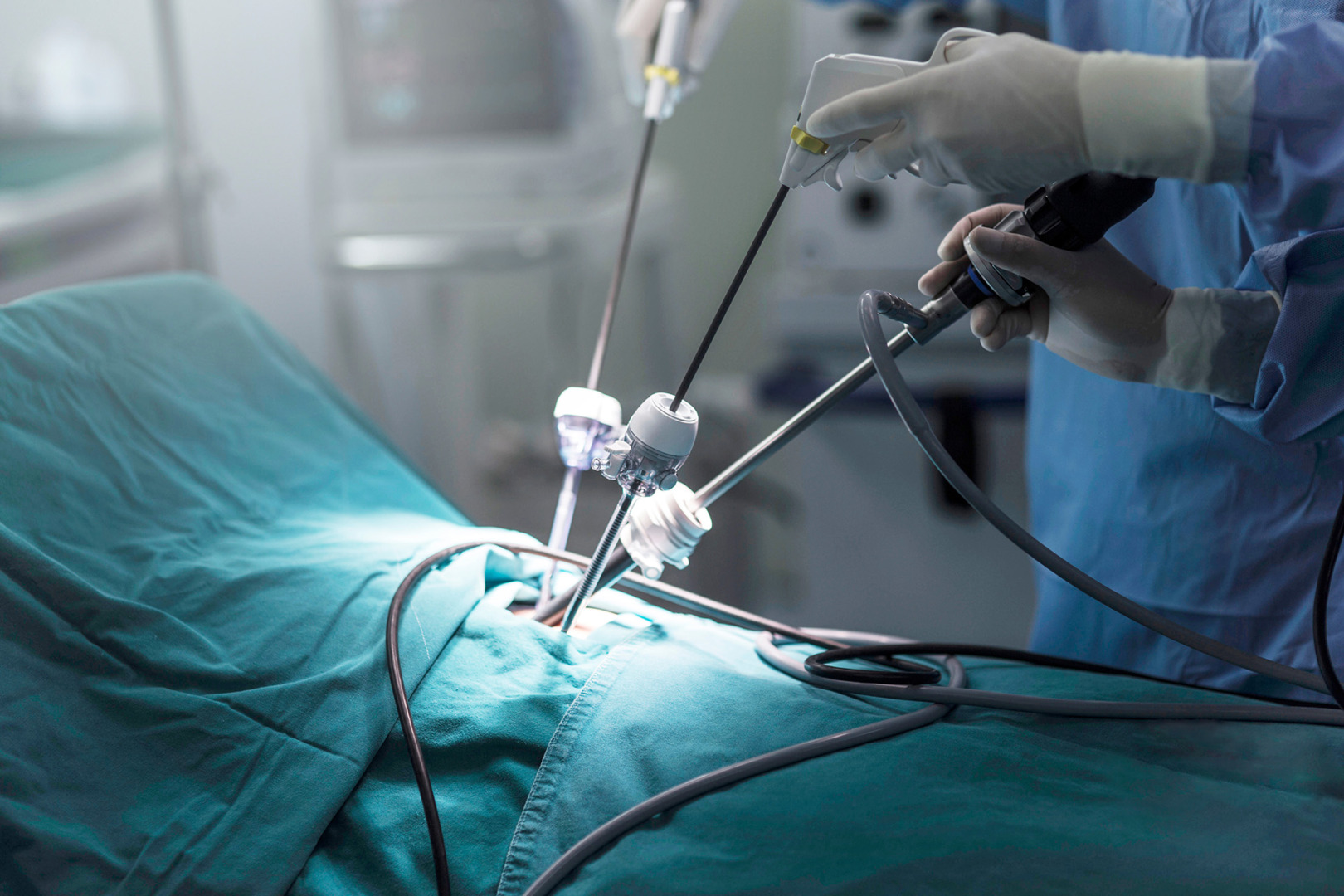
Thoracoscopic Biopsy (VATS)
Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS) is a minimally invasive surgical approach that utilises small incisions and a camera to obtain tissue samples. This advanced surgical method offers high accuracy, allowing the surgeon to view the lung directly, making it a suitable option for more complex cases.
Robotic-Assisted Biopsy
Robotic-assisted technology (RATS) is used to give more precision. The surgeon’s hands control robotic instruments that can reach deep-seated lesions with high accuracy, often improving diagnostic yield.
Open Surgical Biopsy
In rare cases, when less invasive methods are not suitable, an open biopsy may be needed. This involves a larger incision in the chest wall, usually under general anaesthesia. Your specialist will walk you through how to prepare for an open surgical biopsy.
Preparing for a Lung Biopsy
Before a lung biopsy procedure, your care team will take a detailed medical history, review your medications, and perform blood tests to ensure your safe healing and minimise risks. You may be advised to stop certain medications like blood thinners to reduce the risk of bleeding. Your doctor will explain what to expect on the day to help ease anxiety and prepare you for recovery.

Risks and Complications
While lung biopsy procedures are generally safe, there are risks, as with any medical procedure. These may include bleeding, infection, chest pain, or a collapsed lung (pneumothorax). Most of these complications are rare and can be treated. At specialist centres like Neumark Lung & Chest Surgery Centre, advanced techniques and close monitoring reduce risks and ensure patient safety.
Recovery After a Lung Biopsy
Recovery time depends on the type of biopsy. Many patients can go home the same day, especially after bronchoscopic or needle biopsies. Some may need an overnight hospital stay for observation. You may feel some discomfort or soreness at the biopsy site, which should improve within a few days. Most people can return to normal activities within a week, but your doctor may advise you to avoid strenuous exercise until you are fully healed.
Understanding the Results
The results of the lung biopsy procedure typically take a few days to a week. The pathology report will indicate whether the tissue is benign, cancerous, infected, or inflamed.
- Benign Findings: May need follow-up
- Malignant Findings: Will guide treatment, which may be surgery, chemo, radiation or targeted therapies
- Infectious or Inflammatory Conditions: Can be treated with antibiotics or steroids
Getting the results can be tough. At Neumark, we will present the results clearly and compassionately, enabling you to make informed decisions.

Minimally Invasive Advances
Minimally invasive techniques, such as VATS and RATS, have revolutionised the way lung biopsies are performed. They provide smaller incisions, a quicker recovery, and more accurate sampling, especially for deep lesions. They also reduce trauma to healthy tissue, preserve lung function, and offer more comfort to patients. RATS and VATS, thanks to their small incisions, also result in less scarring and a swifter recovery time.
At Neumark, we use the latest technology to deliver optimal care, safe procedures and accurate diagnoses.
Lung Biopsy Procedure and Lung Cancer
When lung cancer is suspected, the biopsy not only confirms cancer cells but also determines the type and stage of cancer. This is important because the treatment varies between small-cell and non-small cell lung cancers. Molecular testing on biopsy samples may also reveal genetic mutations, which guide the development of targeted therapies that improve patient outcomes.
The Role of a Specialist Centre
Choosing the right centre for your lung biopsy procedure can make a significant difference. A specialist thoracic surgery centre, such as Neumark, offers:
- Minimally invasive and advanced surgical expertise
- Latest imaging and robotic technology
- Multidisciplinary team of surgeons, oncologists, radiologists and pathologists
- Patient support from diagnosis to recovery
Prognosis and Next Steps
The biopsy itself doesn’t change the prognosis, but it sets the stage for treatment. Those with malignant disease benefit most from early detection, where treatment options are more and outcomes are better. Those with benign findings find relief in knowing it’s not life-threatening but can still be monitored for changes.
Take the Next Step in Your Care
A lung biopsy is a key diagnostic tool for identifying and treating lung conditions. It gives you clarity to move forward with confidence, whether it’s a benign nodule, infection, or a more serious condition like lung cancer.
At Neumark Lung & Chest Surgery Centre, we provide compassionate, precise and advanced care. If you or a loved one has been recommended a lung biopsy, book a consultation. Our team of thoracic specialists will guide you every step of the way, ensuring you feel informed, supported, and cared for throughout the entire process.

