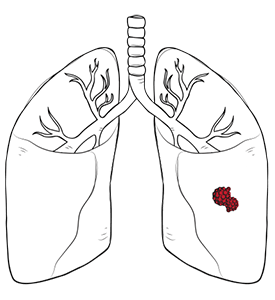

Empyema thoracis is a condition in which, due to bacterial infections, pus accumulates within the pleural space between the lung and the inner chest wall. This empyema lung disease is very serious and necessitates immediate treatment to prevent severe and permanent consequences. Early detection and management from a lung and chest specialist are key to minimising the risk of complications and achieving optimal health outcomes.
The pleural space lies between the lungs and the inner chest wall. In certain patients, an infection of the lung, such as bacterial pneumonia or tuberculosis, can spread and extend to the pleural space. Once the pleural space becomes infected, pus can accumulate, resulting in a condition known as chest empyema. Occasionally, this empyema of the lung can stem from an acute injury to the chest area.
It is an extremely dangerous disease and must be treated quickly to improve the odds of survival and decrease the chances of permanent lung damage.
Empyema thoracis causes include infection reaching the pleural space. Intrinsic causes of empyema include pneumonia, lung abscess, or chronic lung disease. Extrinsic causes of empyema thoracis involve chest trauma, complications after thoracic surgery, or infection introduced during medical procedures.
Certain groups of patients are at higher risk for developing empyema thoracic conditions. Older adults, individuals with weakened immune systems, and those with chronic lung conditions are particularly vulnerable. Patients with a recent history of pneumonia, lung abscess or thoracic surgery are also at increased risk. Additionally, trauma to the chest wall can create a pathway for bacteria to enter the pleural cavity, further raising the likelihood of empyema.
The mortality rate for empyema thoracis remains significant, ranging from 6% to 24%, especially when diagnosis or treatment is delayed. The condition is often associated with other serious infections, such as pneumonia, which can complicate recovery and increase healthcare costs.
Empyema thoracis symptoms often include fever, chest pain, persistent cough and shortness of breath. As the infection progresses, pus may thicken and coat the lungs, making breathing increasingly difficult. Other empyema symptoms can include fatigue, weight loss, night sweats, and, in severe cases, cyanosis or altered mental status due to poor oxygenation.
Effusions, particularly parapneumonic effusions, are a common precursor to the symptoms of empyema thoracis. These effusions can progress and lead to the development of empyema if not managed appropriately.
One of the peculiar symptoms of empyema thoracis is unintended weight loss. Patients with empyema experience a loss of appetite and struggle to eat. This is more common in cases of complex empyema, where the inflammation becomes more severe and the chest cavity can start to scar.
As mentioned, it’s essential to receive treatment for empyema thoracis promptly before the condition worsens and risks permanent damage.
In some cases, empyema thoracis can lead to sepsis. Sepsis is when your body’s immune system goes into overdrive trying to quell an infection, resulting in a high fever, confusion, difficulty breathing, and, in its most severe cases, organ failure.
Empyema thoracis can also lead to a collapsed lung, due to the build-up of pus in the pleural space, causing compression of the lung. A collapsed lung is a life-threatening event. It is best to do all you can to prevent it from occurring in the first place. If you suspect you have empyema thoracis, consult a medical specialist to diagnose your condition.

Empyema thoracis stages progress through three distinct phases, each representing a progressively more severe level of disease. The exudative stage involves the collection of thin, infected fluid in the pleural space. During this stage, effusions accumulate as a result of the inflammatory process. These stages also reflect the progression of parapneumonic effusions, which can develop into empyema if not properly managed.
The fibrinopurulent stage follows, where pus thickens and fibrous septations form, trapping the lung. The final organising stage leads to scar tissue and pleural thickening, with the pleura becoming fibrotic and forming a restrictive peel, which limits lung expansion and makes treatment more complex.
The stages of empyema in adults and children may differ in presentation and progression, requiring tailored management strategies.
Your surgeon will begin by listening to your chest with a stethoscope to detect any abnormalities and review your medical history. If you have had pneumonia recently or are recovering from it, it increases the chances that you have empyema thoracis.
Following this, your doctor will order a CT scan of the chest and a blood test to check for an infection by monitoring your white blood cell count and inflammatory markers in the blood. C-reactive protein should be measured to assess inflammation and help determine the severity of infection. In some cases, your doctor may recommend a thoracentesis, a procedure that involves extracting fluid from the pleural space using a needle and a syringe.
If it is determined that you have empyema thoracis, the treatment will focus on two key areas. First, removing the fluid from the lungs and combating the infection typically involves the use of antibiotics. Removing the fluid requires surgery, though the scale of the empyema thoracis surgery depends on the severity of your condition. Empyema and other complicated infections often require surgical intervention when medical management is insufficient.
For some patients, it is a lighter surgery where the surgeon can drain the fluid via a needle or a chest tube from the patient’s chest. In other cases, a more extensive operation may be necessary after draining the fluid. One such surgery is lung decortication, where the surgeon drains the fluid and removes the infected material encasing the lung.
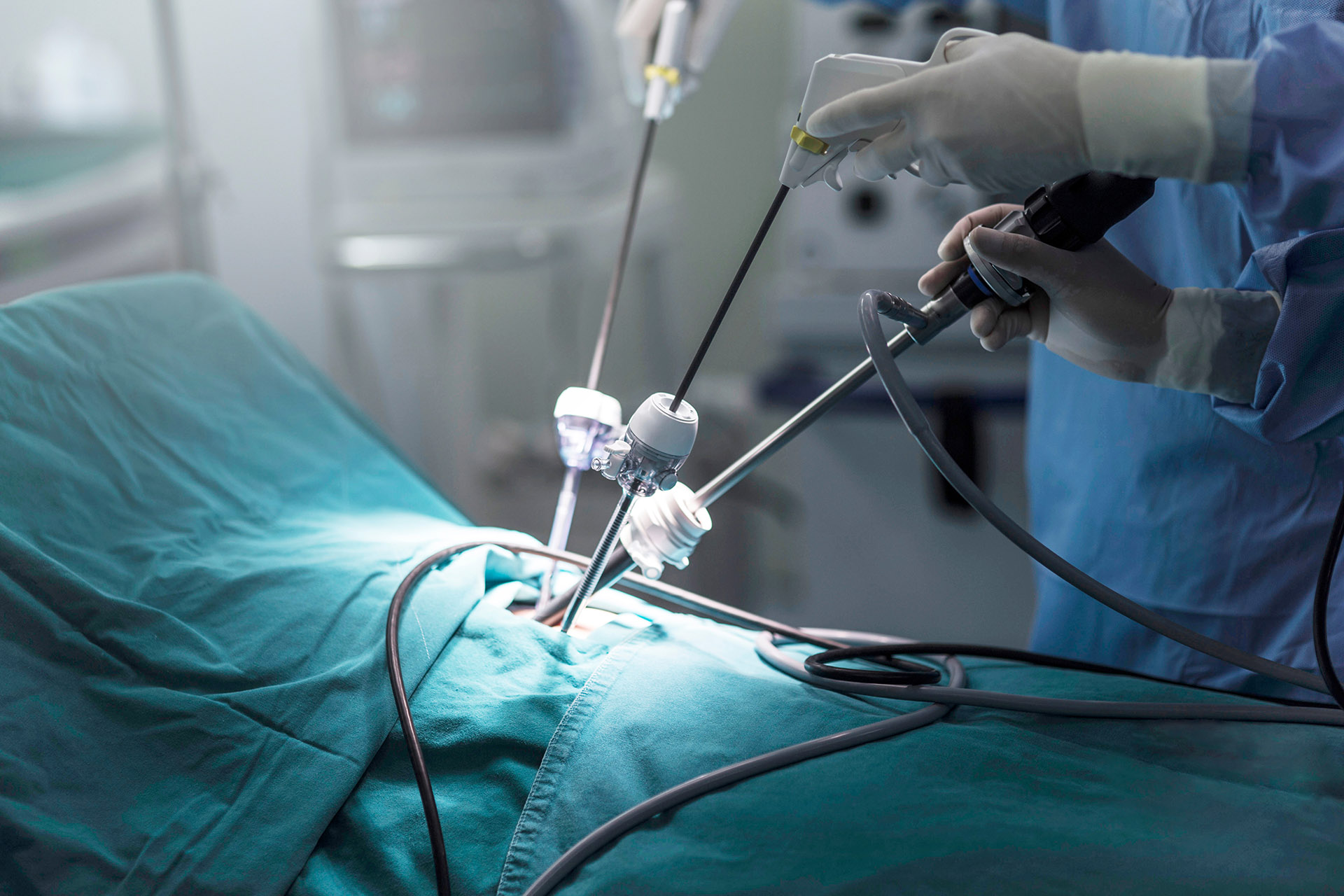
Surgery should be considered when there is persistent infection or when less invasive treatments have failed. Staphylococcus aureus is a common pathogen considered in surgical planning due to its association with complicated pleural empyema. The surgical management of pleural empyema involves careful removal of infected material and restoration of lung function.
Neumark Lung & Chest Surgery Centre surgeons will perform minimally invasive thoracic surgery via a Uniportal Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (U-VATS) approach, utilising the latest technology to ensure a safe and successful treatment. Empyema thoracis can be treated safely and effectively, as long as you seek treatment quickly.
Empyema thoracis typically originates from a primary disease affecting the lungs, such as pneumonia. It occurs when pus accumulates in the pleura, the membrane surrounding the lungs. It can also happen after chest surgery.
Yes, you can be ‘cured’ from empyema thoracis, though it is vital you seek surgical treatment early to prevent the condition from having permanent effects. Through a combination of surgery and antibiotics, empyema thoracis can be effectively treated, relieving the lungs of pus and combating the infection.
Empyema thoracis is a severe condition for all individuals, but it is associated with heightened risk factors. Mortality rates of thoracic empyema are significant, especially without prompt treatment. Patients who are immunocompromised are especially at risk, as their bodies will have a harder time fighting the infection. For that same reason, persons with diabetes are also at greater risk of permanent complications arising from empyema thoracis.
Certain age groups, such as young children and older adults, are at higher risk for developing empyema thoracis. Other risk factors include underlying lung disease, immunosuppression and chronic illnesses.
After completing a regimen of antibiotics and your surgery, you may need to return for an additional X-ray to ensure that all the infected fluid has been drained and the lungs have expanded properly. It’s essential to follow your doctor’s instructions during recovery to prevent further complications from arising after surgery.
Complications of thoracic empyema can include lung scarring, reduced lung function and persistent infection. In severe cases, complications may lead to sepsis or respiratory failure.
DISCLAIMER: The information provided on this website is for general informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. The use of this website does not create a doctor-patient relationship and no medical advice should be inferred or assumed. It is the user’s sole responsibility to seek the advice of their healthcare professionals for any medical concerns they may have and the user should not disregard, or delay, prompt medical advice for any such condition.
Neumark Lung and Chest Surgery Centre benefits from the expertise of a multidisciplinary team led by Dr Harish Mithiran, senior consulting thoracic surgeon at Gleneagles Hospital and Mt Alvernia Hospital.
Neumark is a lung and chest specialist centre with access to leading treatment modalities to achieve the best possible outcomes for lung disease and preventative patient screening.
Our foremost priority is to treat your condition as effectively as possible. Schedule a private consultation today; complete the form below, call, +65 6908 2145; WhatsApp, +65 9726 2485; or email, info@neumarksurgery.com.
Gleneagles Medical Centre
6 Napier Road
#02-09 Gleneagles Medical Centre
Singapore 258499
Mount Alvernia Hospital
820 Thomson Road
#06-07 Medical Centre A
Singapore 574623