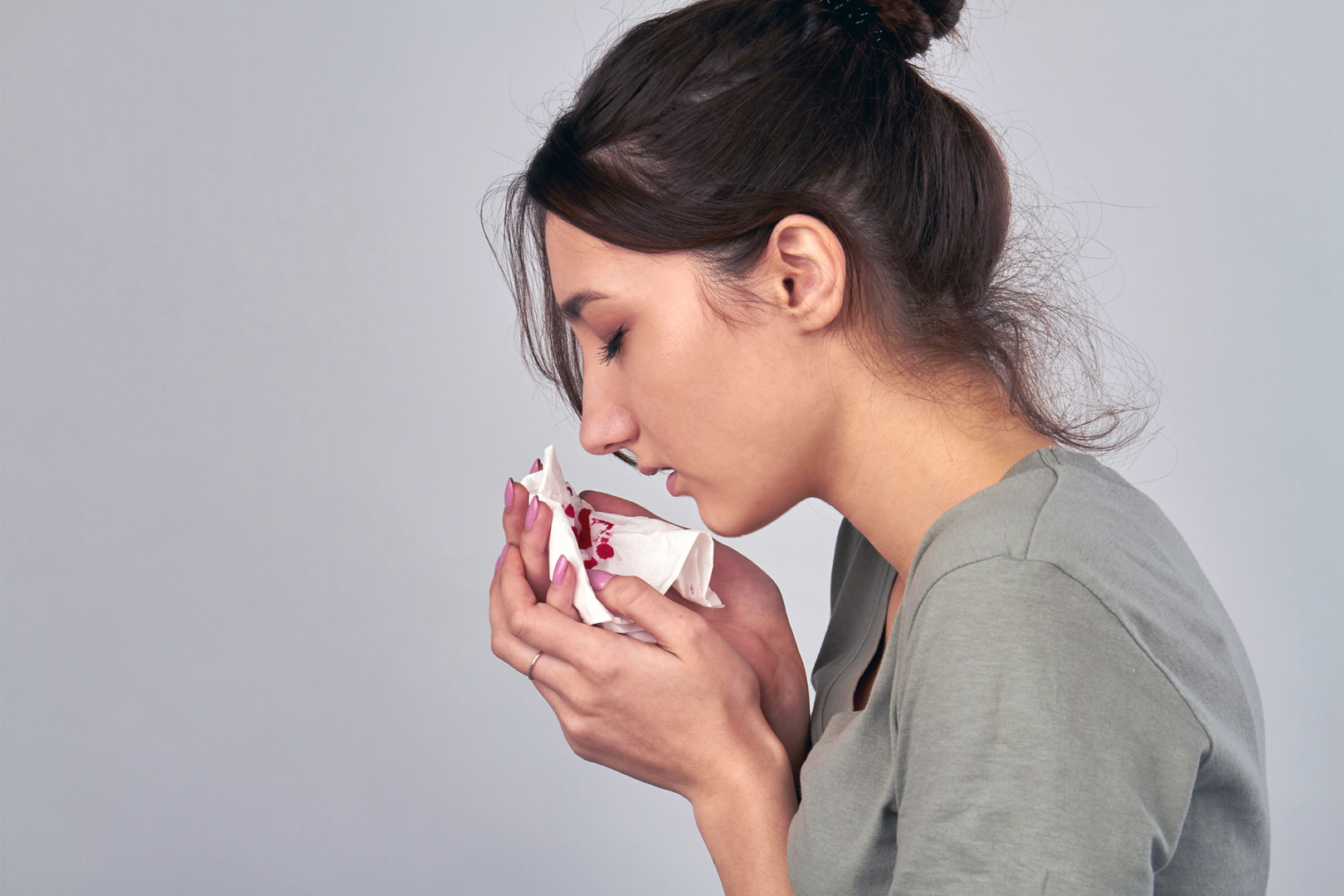
Seeing blood when you cough is unsettling. Whether it occurs once or recurs, coughing up blood often indicates an underlying condition that requires medical evaluation. Persistent or heavy bleeding may indicate something more serious, such as lung cancer or a severe respiratory condition.
If you are wondering what happens if you cough up blood, the answer depends largely on the cause, severity, and frequency of the symptom. Some cases may require urgent intervention, whereas others may require only monitoring and medical treatment.
What is Coughing Up Blood?
Coughing up blood, medically known as hemoptysis, involves expelling blood or bloody mucus from the lower respiratory tract, which comprises the lungs and throat. This symptom can be alarming, but it is important to understand that it has many potential causes, some of which are not serious.
The blood coughed up is often frothy or bubbly, mixed with mucus or saliva, and can range in colour from pink to red to rust-coloured. While the amount of blood is usually small, coughing up large amounts is a serious condition that requires immediate emergency medical attention. Recognising the characteristics of hemoptysis can help in seeking timely and appropriate care.

What Makes One Cough Up Blood?
While the occasional coughing up of blood due to a minor irritation may not be an emergency, certain red flags indicate a need for urgent medical intervention. Hemoptysis can originate from various conditions affecting the lungs and airways. The most common causes of coughing up blood include:
Acute and Chronic Respiratory Infections
- Bronchitis: A persistent cough associated with acute bronchitis may occasionally produce small streaks of blood in the sputum due to airway inflammation. Bronchitis and coughing up blood are often associated and warrant further evaluation and treatment.
- Pneumonia: Infections that inflame the lungs can cause blood-tinged sputum and are often accompanied by fever and difficulty breathing.
- Tuberculosis (TB): A bacterial infection that can lead to severe hemoptysis if left untreated.
Chronic Lung Diseases
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): COPD causes long-term lung damage that can result in hemoptysis, particularly in advanced cases. A symptom of COPD is coughing up blood, which may indicate the stage of the disease.
- Bronchiectasis: A condition where the airways become abnormally widened, leading to chronic infection and bleeding.
Lung Cancer: The Most Serious Concern
- Lung Cancer: One of the hallmark symptoms of lung cancer is coughing up blood, caused by a tumour eroding nearby blood vessels. Persistent coughing, unexplained weight loss, chest pain, and hemoptysis should always prompt immediate medical evaluation.
Post-Surgical and Procedural Bleeding
- Coughing Up Blood after A Lung Biopsy: A lung biopsy, performed to diagnose conditions like lung cancer, can sometimes result in temporary hemoptysis.
- Coughing Up Blood after Surgery: Postoperative bleeding can occur, particularly after lung-related surgeries or procedures affecting the respiratory tract.
Blood Clots and Cardiovascular Issues
- Pulmonary Embolism: This life-threatening condition, in which a blood clot blocks an artery in the lung, can lead to sudden hemoptysis and breathlessness.
- Heart Failure: Certain forms of heart failure, such as mitral stenosis, can cause pressure buildup in the lungs, leading to blood-streaked sputum.
Seek immediate care if you experience heavy or recurrent coughing up blood, defined as coughing up at least a few teaspoons of blood. Difficulty breathing, persistent shortness of breath, or unexplained chest pain also warrant immediate attention. Additionally, symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, persistent fatigue, dizziness, or fainting may suggest a serious underlying condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Risk Factors for Hemoptysis
Several factors can increase the risk of developing hemoptysis.
Smoking can cause extensive damage to the lungs and elevate the risk of lung cancer, leading to the coughing up of blood. As mentioned, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lung cancer itself, and severe infections like pneumonia can also lead to coughing up blood.
Additionally, cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder characterised by thick, sticky mucus buildup in the lungs, increases the risk of hemoptysis. Blood clotting disorders, such as haemophilia, can further exacerbate the likelihood of this condition. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for early detection and prevention.
Diagnosing the Root of the Problem
Diagnosing the cause of hemoptysis requires a comprehensive approach that includes a physical examination, medical history, and various diagnostic tests.
During the physical exam, the doctor will check for signs of lung disease or other conditions that may be the cause of the bleeding. The patient’s medical history, including prior lung diseases or conditions, can provide valuable insights.
Diagnostic tests play a significant role in pinpointing the cause. To determine the cause of hemoptysis, a doctor may recommend several diagnostic tests, including:
- Chest X-rays and CT Scans: To detect infections, lung abnormalities, or tumours
- Bronchoscopy: A procedure that involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera into the airways for direct visualisation of the lungs and airways to locate the source of bleeding
- Sputum Tests: To identify bacterial infections such as tuberculosis
- Blood Tests: To identify underlying conditions such as anaemia, blood clotting disorders, and overall lung function
Treatment Options for Coughing Up Blood
The treatment for coughing up blood depends on the underlying cause. Antibiotic and supportive care are typically prescribed for infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis or tuberculosis. In cases where coughing up blood is due to lung cancer, a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies may be required. If bleeding is severe, a bronchial artery embolisation (BAE) may be performed to occlude the bleeding vessel and control the haemorrhage.
Patients with COPD-related hemoptysis often benefit from oxygen therapy, bronchodilators and pulmonary rehabilitation to both manage symptoms and reduce future occurrences. In situations where the bleeding is significant or life-threatening, surgery to remove the affected lung tissue may be necessary to ensure the patient’s safety.

Complications
Coughing up blood can lead to several serious complications if not promptly addressed. One of the most concerning is the formation of blood clots in the lungs, which can be life-threatening. Severe hemoptysis can also result in respiratory failure. Additionally, the risk of infection increases, particularly if the underlying cause is a lung infection.
Another potential complication is the development of a lung abscess, a pocket of pus that forms in the lungs, which can further complicate the patient’s condition. In some cases, hemoptysis can lead to vomiting blood, which necessitates urgent care.
Given these potential complications, it is imperative to seek immediate medical attention if you experience these symptoms.

The Role of Early Detection in Lung Cancer and Serious Conditions
Early detection is critical, especially when lung cancer is a potential concern. The earlier lung cancer or other serious respiratory conditions are diagnosed, the more effective the treatment can be. Regular lung screenings, particularly for high-risk individuals like smokers and those with a family history of lung disease, can be life-saving.
At Neumark Lung & Chest Surgery Centre, our specialists use advanced diagnostic tools to ensure timely detection and tailored treatment plans for every patient.
When to Seek Expert Thoracic Care
Whether it is a one-time or recurring occurrence, coughing up blood warrants seeking medical expertise to identify the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment.
At Neumark Lung & Chest Surgery Centre, we are committed to ensuring the best possible care for our patients, from lung cancer screenings to minimally invasive surgical treatments. Our team of experienced thoracic specialists is dedicated to providing advanced diagnostic evaluations and personalised treatment plans. Contact Neumark today for a comprehensive evaluation.

