Our lungs are precious organs that keep our body operating. However, in some cases, like with lung cancer, portions of the lung need to be removed to protect the rest of the body. In these situations, a lung cancer wedge resection, a precise surgical procedure, removes a small, wedge-shaped (triangular) portion of lung tissue. This approach targets a limited lung area, making it an ideal option when the disease is caught early or confined to a specific region. The goal of wedge resection of the lung can vary, from obtaining a biopsy to confirm a diagnosis to removing a localised mass or tumour for therapeutic reasons.
What is a Lung Cancer Wedge Resection?
In simple terms, a lung cancer wedge resection involves surgically excising a small portion of lung tissue, typically in the shape of a wedge, hence the name. This removed tissue may contain suspicious nodules, lesions, or tumours that warrant further examination or removal. Since the procedure removes only a small section of the lung, it spares much of the surrounding healthy lung tissue, making it less invasive than other lung surgeries that remove entire lobes or segments.
Reasons for a Lung Cancer Wedge Resection
This form of lung resection surgery is often recommended when there is an abnormal area in the lung that may represent a tumour, infection or other condition that cannot be thoroughly evaluated or treated by less invasive means. Below are some common scenarios where a wedge resection might be beneficial:
- Metastatic Tumours: If cancer from another site has spread (also known as metastasised) to the lungs, but the original site has been treated, a wedge resection can remove the localised tumour without requiring extensive lung removal.
- Bullous Disease of the Lung: Bullae are air-filled sacs or ‘blisters’ that form within the lung tissue. In some cases, these bullae can rupture, causing the lung to collapse. A wedge resection removes the area affected by the bullae, helping to prevent further collapses and improve lung function.
- Early-Stage Lung Cancer: For patients with small, localised lung cancers, a wedge resection may effectively remove the cancerous tissue. This approach can help preserve lung function and avoid more extensive surgery.
- Lung Nodules or Lesions: Localised nodules or lesions may not always be cancerous but may require removal for a thorough diagnosis or because they pose a risk if left untreated. A wedge resection allows for both the removal and microscopic examination of these areas.
- Tuberculosis (TB): In rare cases, a drug-resistant or untreatable form of tuberculosis may necessitate surgical intervention. If the TB is confined to a specific area, a wedge resection may remove the affected tissue, reducing symptoms and potentially preventing further lung damage.
When is a Wedge Resection Most Effective?
Wedge resection is particularly beneficial when the disease is detected early and confined to a small, isolated lung region. In early-stage lung cancer treatment, for instance, a wedge resection can be highly effective, offering a less invasive solution with fewer long-term impacts on lung function. Early detection is a significant factor in determining the effectiveness and suitability of lung wedge resection surgery. If the disease has spread extensively within the lungs or other parts of the body, this type of surgery is generally not recommended.

Minimally Invasive Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS)
A pulmonary wedge resection can be performed using video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS). This minimally invasive technique involves tiny incisions of approximately 3 to 4 centimetres to insert a small camera (thoracoscope) and other specialised surgical instruments. The camera lets the surgeon view the lung area on a monitor in real time and perform precise surgical movements. VATS offers several benefits:
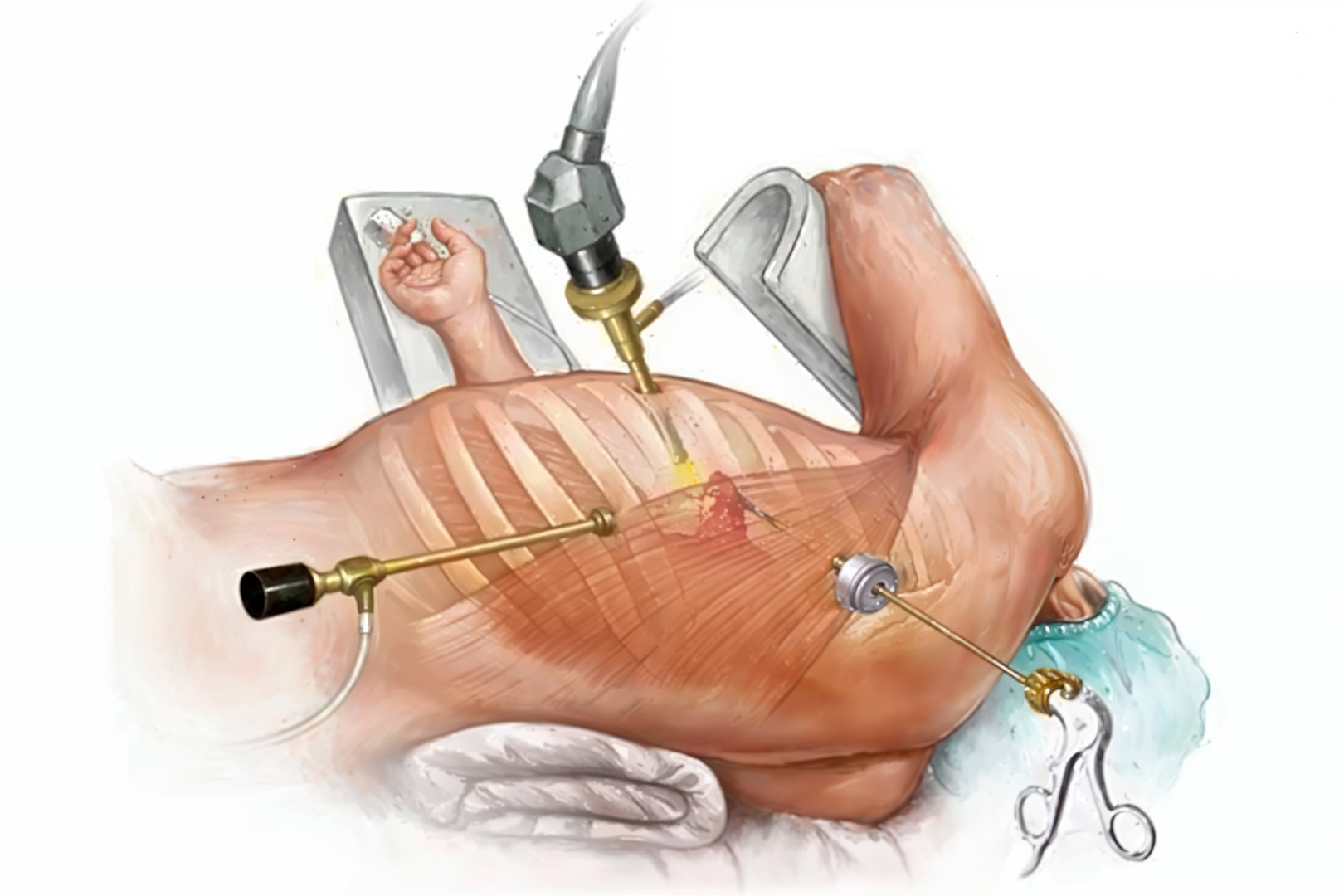
- Smaller Incisions: With only a few centimetres incisions, patients experience less pain post-surgery and have reduced scarring.
- Shorter Recovery Time: Minimally invasive procedures like VATS generally lead to faster recovery, allowing patients to resume daily activities sooner.
- Lower Risk of Complications: VATS tends to carry a lower risk of infection, bleeding and other complications, making it a safer alternative for many patients.
- Improved Precision: The camera allows surgeons to view the lung area in detail, enhancing precision and accuracy during the resection.
For these reasons, VATS has become the preferred method for wedge resections and other thoracic surgeries in recent years, particularly for patients who are good candidates for minimally invasive procedures.
What to Expect Before and After a Wedge Resection
While less invasive than other lung surgeries, a wedge resection is still significant. To ensure the best outcome, patients should expect a series of pre- and post-operative protocols, all designed to support their recovery.
Pre-Operative Preparation
Before surgery, patients undergo imaging studies, such as CT scans, and may need pulmonary function tests to assess lung capacity and function. Smoking cessation is typically advised, as smoking can increase surgical risks and delay healing. In addition, patients may also be asked to avoid certain medications that could increase bleeding risks.
Post-Operative Care
After surgery, patients are closely monitored for complications, and many can return home within a few days. Breathing exercises and light activity are encouraged early in recovery to help maintain lung function and promote healing. Physical restrictions, such as avoiding heavy lifting, are common in the weeks following surgery to allow incisions and lung tissue to heal properly.
The Importance of Early Detection and Diagnosis
The effectiveness of a wedge resection hinges significantly on early detection and diagnosis. For example, identifying lung cancer at an early stage can mean a higher likelihood of successful removal with a limited resection like a wedge. Routine screenings and proactive attention to lung health can make a substantial difference, especially for individuals at high risk of lung disease.
Neumark’s Lung Cancer Treatment Centre specialises in advanced surgical techniques such as VATS-guided wedge resections, ensuring each patient receives a personalised, evidence-based approach to lung health. If you’re considering or have been recommended for a wedge resection, the Neumark team is here to provide expert guidance for your health and recovery.