
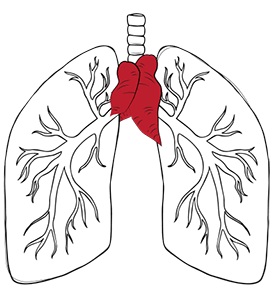
The thymus is a small gland just under the breastbone (sternum) and in front of your heart. Its main purpose is to produce immune cells as the body develops, and it typically shrinks as the body grows.
A thymectomy is a surgical procedure involving the removal of the thymus gland. The thymus, a lymphoid organ situated in the anterior mediastinum, posterior to the sternum and anterior to the great vessels, plays a crucial role in the development of the immune system.
The thymus gland is bilobed and composed of lymphoid tissue. Its primary function is the production and maturation of T-lymphocytes, critical components of the adaptive immune system. The gland is most active during fetal development and early childhood and reaches its maximum size at puberty.
During early childhood into puberty, the thymus undergoes a process known as thymic involution. This physiological change involves the gradual replacement of thymic tissue with adipose tissue. Despite this involution, residual thymic tissue continues to function throughout adulthood, albeit at a reduced capacity.
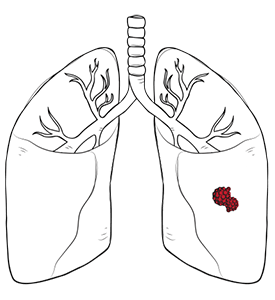
For some people, the thymus may present a problem. The gland can either develop a tumour, malignant or benign, which may warrant thymus removal surgery.
Myasthenia gravis occurs when immune cells begin to attack the connections between nerves and muscles. This leads to weaknesses in various muscle groups across the body and may warrant treatment. Thymus surgery for myasthenia gravis can help reduce symptoms by decreasing antibody production, providing longer-term relief than some other treatments.
In both situations, the solution for most patients is to remove the thymus, especially since it no longer serves a purpose in most adults.
Preparing for a thymectomy involves several important steps to ensure patient safety and the best surgical outcome. Before the thymectomy procedure, patients will undergo a comprehensive medical evaluation, which may include a physical examination, blood tests and imaging studies such as chest X-rays or CT scans to assess the thymus gland and the surrounding tissues.
Additional tests, like pulmonary function tests or cardiac assessments, may be ordered to evaluate the patient’s overall health and readiness for thymus surgery. Patients are typically advised to stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners, and to refrain from eating or drinking for a specified period before the operation. Following the instructions provided by healthcare providers is essential for a smooth, successful thymectomy.
Neumark surgeons perform the thymectomy using the most advanced technology to ensure a safe surgery. There are several approaches to performing a thymectomy, each tailored to the patient’s specific needs and the surgeon’s expertise.
Minimally invasive robotic and VATS thymectomy are the recommended courses of treatment, but open thymectomies are also performed when necessary based on thymectomy indications.

Whichever method is chosen, the intended goal of the surgery is thymus removal, either to remove a growing tumour during thymoma surgery or to prevent the thymus from mistakenly producing the immune cell response that causes myasthenia gravis. Surgery typically lasts between 1 and 3 hours. At the end of the procedure, the breathing tube is generally removed in the operating room, and patients may require oxygen and monitoring during recovery. Patients may be given pain medications to manage discomfort after surgery, and a stay in the hospital overnight or for a short period is often needed for observation.
If you are concerned about your thymus, visit us at Neumark Lung & Chest Surgery Centre to speak with one of our surgeons to find out if a thymectomy is right for you. Selecting the appropriate treatment plan tailored to your health is crucial for achieving the best possible outcomes.
Related Thymectomy
At Neumark, we use advanced solutions through innovative technologies to achieve healthy outcomes for our patients. For example, some surgeons may conduct open surgery via a median sternotomy approach for a thymectomy, which increases the potential risk. In contrast, robotic thymectomy (RATS) or VATS thymectomy only involves smaller incisions, speeds healing time and reduces the recovery process. The thymectomy success rate and risks depend on the patient’s health. Speak with our surgeon today about any of your concerns to determine if a thymectomy is the proper treatment for you.
Myasthenia gravis remission after thymectomy is a promising development in the treatment of the autoimmune chronic condition. Recent studies have also uncovered that the timing of thymectomy in myasthenia gravis may be an important factor. Thymectomy, the surgical removal of the thymus gland, can improve symptoms of myasthenia gravis by halting the production of antibodies that attack the neuromuscular junction. However, the level of improvement or remission varies from patient to patient. The decision to undergo thymectomy should be made with the guidance of a thoracic specialist or surgeon. Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of thymectomy on myasthenia gravis and its potential for inducing remission.
Recovery differs from person to person. Some patients may have to stay overnight in the hospital following a thymectomy for observation and to ensure a healthy recovery. All patients will be advised to avoid strenuous physical activity following a thymectomy to ensure optimal recovery. Scarring for most patients is minimal, since robotic thymectomy and VATS thymectomy only involve minor incisions. The risk of recurrence of a thymoma following a thymectomy would depend on the stage and type of thymoma. For peace of mind, your surgeon will likely ask you to schedule a CT scan every five years to ensure that there are no recurrences.
It is very important to consult your healthcare provider about which medicines you should stop or continue before a thymectomy, especially if you have conditions like myasthenia gravis. Some medications may need to be adjusted or temporarily discontinued to reduce surgical risks and ensure your safety. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding your medicine before surgery.
Thymectomy side effects and thymus removal side effects are important considerations, as thymectomy is not without risks and potential complications, including pain, fatigue, difficulty swallowing, bleeding, infection, or injury to nearby structures. Some patients may also experience anaesthesia-related or underlying medical condition-related complications. Therefore, a thorough assessment of potential risks and benefits with healthcare providers is crucial when considering thymectomy as a treatment option.
DISCLAIMER: The information provided on this website is for general informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. The use of this website does not create a doctor-patient relationship and no medical advice should be inferred or assumed. It is the user’s sole responsibility to seek the advice of their healthcare professionals for any medical concerns they may have and the user should not disregard, or delay, prompt medical advice for any such condition.
Neumark Lung and Chest Surgery Centre benefits from the expertise of a multidisciplinary team led by Dr Harish Mithiran, senior consulting thoracic surgeon at Gleneagles Hospital and Mt Alvernia Hospital.
Neumark is a lung and chest specialist centre with access to leading treatment modalities to achieve the best possible outcomes for lung disease and preventative patient screening.
Our foremost priority is to treat your condition as effectively as possible. Schedule a private consultation today; complete the form below, call, +65 6908 2145; WhatsApp, +65 9726 2485; or email, info@neumarksurgery.com.
Gleneagles Medical Centre
6 Napier Road
#02-09 Gleneagles Medical Centre
Singapore 258499
Mount Alvernia Hospital
820 Thomson Road
#06-07 Medical Centre A
Singapore 574623