The Discovery of a Lung Nodule: What Comes Next?
Finding out you have a lung nodule can be deeply unsettling. Yet these small lung masses, often detected on routine chest X-rays or CT scans, are quite common. While most are benign, some can be early signs of lung cancer. This is where thoracic surgeons’ expertise becomes evident.
In Singapore, where health screenings are widely accessible, early detection of lung nodules or white spots on your lungs is increasingly common. However, detection is just the first step. The real challenge lies in determining the nature of the nodule, when to be concerned about a pulmonary nodule, and deciding on the best course of action.
Evolution of Lung Nodule Removal Surgery
Traditionally, removing a lung nodule meant a major operation with a large incision. This approach, known as thoracotomy, often resulted in significant post-operative pain and lengthy recovery periods. However, the landscape of thoracic surgery has changed dramatically in recent years, with new technologies designed to enhance patient safety and comfort.
Minimally invasive techniques have revolutionised the treatment of lung nodules, offering patients less pain, a quicker recovery, and better cosmetic results. Two methods in this field are Uniportal Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (U-VATS) and Robotic-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (RATS).
Single Incision U-VATS
Uniportal Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery represents a significant leap forward in minimally invasive thoracic surgery. Unlike its predecessor, which required multiple small incisions, U-VATS requires just one small cut, typically about 3-4 centimetres long. Through this single port, surgeons can insert a high-definition camera and specialised instruments to remove the lung nodule.
The benefits of U-VATS are impressive. Patients often experience less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and a more rapid return to normal activities. The single small incision also results in minimal scarring, a factor that can have a notable psychological impact on patients’ well-being.
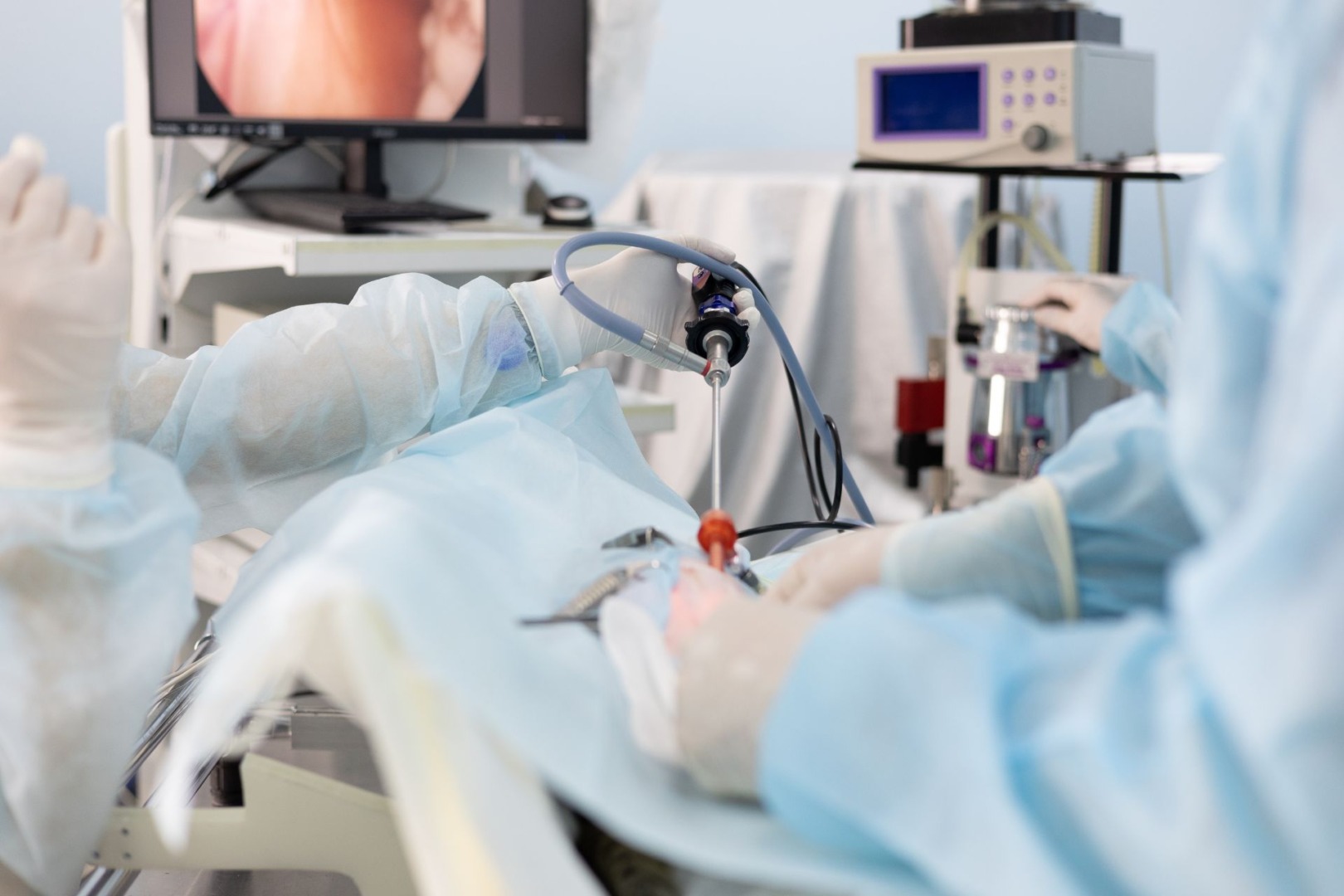
The advantages of U-VATS go beyond patient comfort. For surgeons, this technique offers excellent visualisation of the thoracic cavity. The high-definition camera provides a clear, magnified view, enabling precise removal of the nodule while preserving healthy lung tissue, thereby improving postoperative outcomes.
Precision with RATS
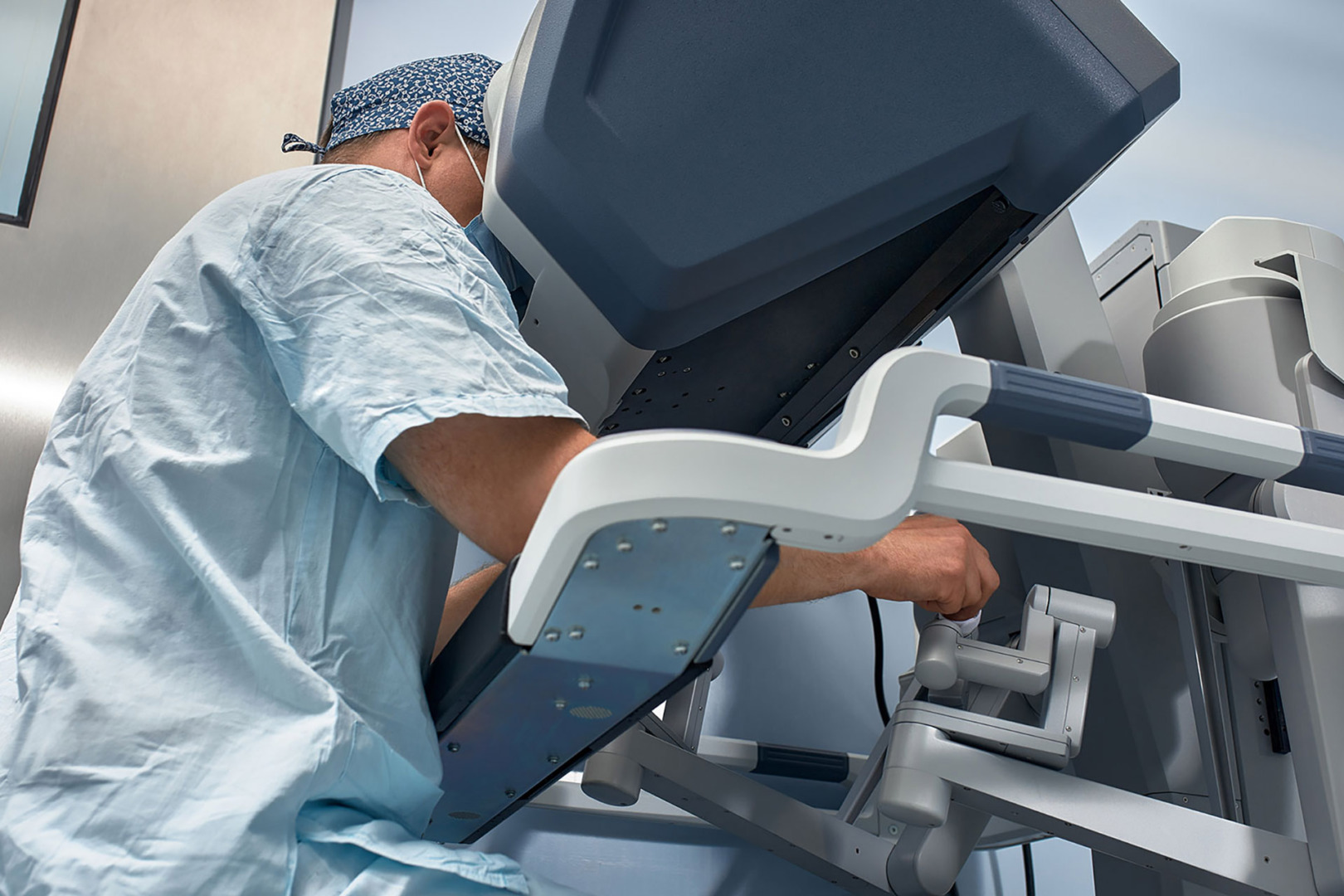
Robotic-Assisted Thoracic Surgery advances minimally invasive techniques. This approach combines the benefits of minimal access surgery with advanced robotic technology. The surgeon controls robotic arms from a console, manipulating them with incredible precision to remove the lung nodule.
RATS offers several unique advantages. The robotic system provides a three-dimensional, high-definition view of the surgical site, enhancing the surgeon’s depth perception. The robotic arms can rotate 360 degrees and bend in ways human hands can’t, providing unparalleled manoeuvrability in the narrow space of the chest cavity.
Patients undergoing RATS often experience benefits similar to those of U-VATS: less pain, faster recovery, and minimal scarring. Additionally, RATS’ precision can be particularly beneficial for complex cases or when the nodule is in a hard-to-reach location.
Choosing the Right Approach for Lung Nodule Removal
While U-VATS and RATS represent significant advancements, it’s important to note that not every patient or every lung nodule is suited to these techniques. Factors such as the nodule’s size and location, the patient’s overall health, and the surgeon’s expertise all play a role in determining the best approach.
In some cases, a traditional thoracotomy may still be the most appropriate lung nodule removal surgery. This is particularly true for larger tumours or in emergencies. The key is having a thoracic surgeon who is well-versed in these techniques and can recommend the most appropriate approach for each case.
It’s not only the surgery itself that has changed. Recovery for patients has significantly improved with minimally invasive techniques after lung nodule removal surgery, provided they follow their thoracic surgeon’s guidance. Many patients who undergo U-VATS or RATS find themselves back on their feet within days rather than weeks. However, carefully following postoperative instructions and attending all follow-up appointments are important to ensure optimal healing.
Importance of Early Detection and Intervention
Regardless of the surgical technique, early detection and intervention are crucial for lung nodules. This is especially true if the nodule proves to be malignant. Early-stage lung cancers are more treatable and have better outcomes.
Given the availability of health screenings in Singapore, individuals are encouraged to undergo regular check-ups. For those with risk factors such as a history of smoking or exposure to certain environmental pollutants, more frequent screenings may be recommended.
If you’re concerned about lung nodules, contact Neumark Lung & Chest Surgery Centre today to schedule a consultation with Dr Harish Mithiran.